Beginner’s educational guide & checklist focusing on opportunities in 2026, risks involved, execution & APIs
Is automated trading legal for individual investors in India? What are the steps to automated trading in India? What are the risks involved? Is this the right path for me? What is the difference between automated trading and AI trading? These are the exact questions Indian traders, developers, and finance professionals are asking as algorithmic and automated trading move from niche to mainstream.
Our intention of writing this guide is to enable absolute beginners, with no hype, no jargon overload. By the end, you’ll clearly understand what automated trading is, how it works in India, whether it’s legal, what you need to understand before jumping into, and the mistakes to avoid in 2026.
Difference between Automated Trading and Algorithmic Trading
Automated Trading: This is when you automate the entire workflow.
Algo Trading: Systematic Trading Logic + Automated Trading
Systematic Trading logic can be created using quantitative techniques, computation power to find an edge or alpha, which is reducing risks and ensuring positive PnL.
The Regulatory Definition: SEBI doesn’t differentiate between algorithmic and automated trading. It defines algorithmic trading as the process of sending orders in an automated manner without any manual intervention.
In 2026, most retail traders in India mean API-based automated execution when they say “algo trading”.
Levels of Automated Trading
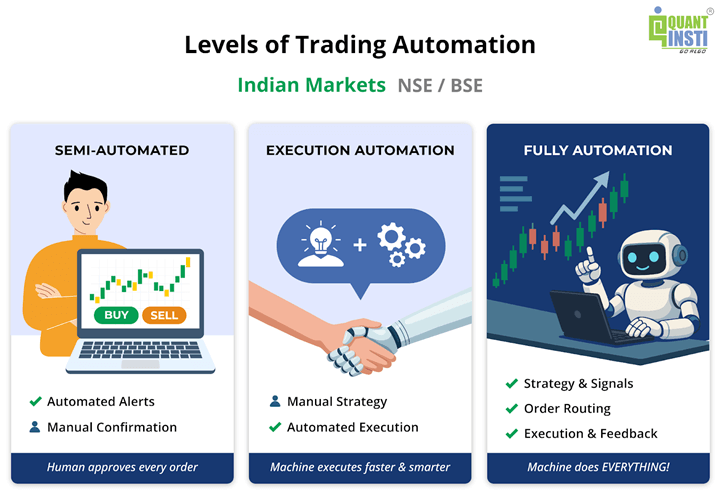
- Semi-automated trading: Human Confirmation is needed.
An algorithm might generate alerts or even pre-fill an order, but a human clicks ‘Confirm’ to actually send it. - Automate just the order execution: Using a broker’s algo for slicing a large order into smaller chunks; usually popular on institutional trading.
- Automate the entire trading process: Strategy/Signal → API Order → Broker → Exchange → Execution → Feedback loop.
Everything happens in seconds or less. By the time a human blinks, an automated system could have evaluated a signal and completed a trade.
Read about the fully automated process in detail here.
What are Trading APIs?
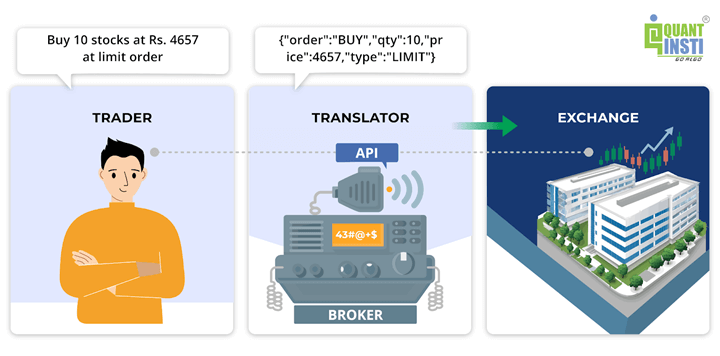
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are the bridges between your trading algorithm and the broker/exchange. They allow your program to fetch market data and place orders in real time. Brokers like Zerodha, Groww, and others now offer APIs so that individuals can connect their algorithms directly to the markets. In fact, India’s regulators have officially recognized API-based retail algo trading as a legitimate approach to market participation.
Read about Indian Brokers & APIs provided by them.
Why is Systematic Trading gaining popularity among individual investors?
1. Eliminating Emotional Bias and enforcing Consistency: Remove human emotion from financial decisions
2. Scientific Validation (The "Eye Deceives" Problem): Prove that a strategy actually works before risking capital.
3. Scalability and Data Processing: Identify hidden patterns and non-linear relationships in market data.
4. Market Efficiency and Cost Reduction: HFT firms employ systematic trading at large trading volumes, enabling them to act as market makers. Because of the efficiency and tighter spreads created by HFTs, average retail traders save significant money (e.g., an estimated $250 per year for an American retail trader) in transaction costs.
5. Adaptation to Market Crowding As markets evolve, simple strategies stop working. Evolve these strategies and find new edges in a tightening market..
In summary, quantitative trading is necessary to transform trading from an art based on "gut feeling" into a business based on statistical probability, operational efficiency, and risk management.
Is automated trading legal in India in 2026?
Yes. Fully legal, for your own account. SEBI officially recognizes retail algorithmic trading via broker APIs, provided you follow certain rules .
| What’s Allowed Personal-use automation with official tooling | What’s NOT Allowed Activities that require registration or bypass rules |
|---|---|
|
|
Note: This is a simple summary for clarity. Always verify requirements with your broker and applicable regulations.
Steps of Automated Trading: Explained
Whether you want to write your own code for automated trading or hire a developer to help you trade using broker’s API, it is essential you understand the entire automated trading process.
At a high level, an automated trade follows a simple pipeline:
Strategy → Broker API → Broker → Exchange (NSE/BSE/MCX/NCDEX) → Feedback
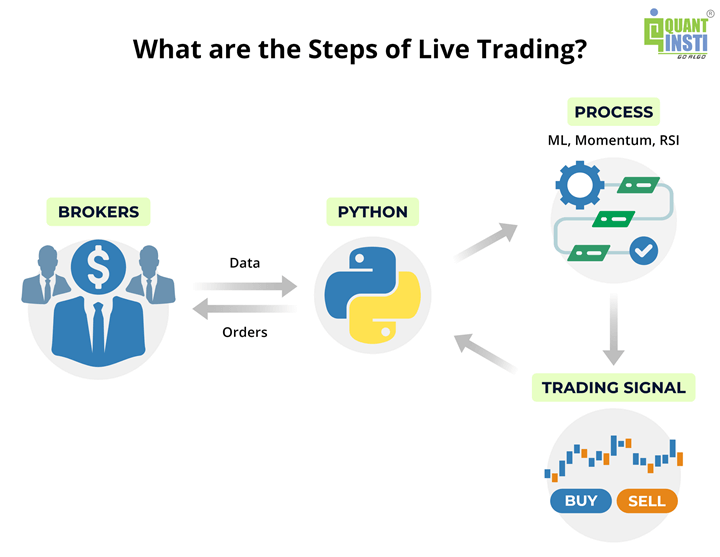
Here’s what happens step by step:
1. Strategy Generates a Signal
Everything starts with a trading strategy written in code (for example, in Python) or configured on a platform. The strategy continuously watches market data like prices or indicators. When your predefined conditions are met, it generates a signal such as:
- Buy 10 shares of Reliance at ₹1500
- Sell NIFTY futures at market price when RSI < 30
The key point: the decision is rule-based and pre-defined, not emotional or manual.
2. Order Is Sent via Broker API
Once a signal is generated, your program sends an order request to your broker using an API (Application Programming Interface).
This API call contains all order details:
- instrument
- quantity
- buy or sell
- order type (market / limit)
This happens in milliseconds, no manual typing or clicking.
3. Broker Checks & Routes the Order
Before sending the order to the exchange, the broker performs basic checks:
- Do you have enough funds or margin?
- Is the order valid as per exchange rules?
- Is it within broker risk limits?
If everything is fine, the broker assigns the order an ID (and an Algo tag, as required by regulations) and forwards it to NSE or BSE.
4. Exchange Executes the Trade
At the exchange:
- Market orders execute immediately at available prices.
- Limit orders wait until the price condition is met.
Execution is handled entirely by the exchange’s matching engine. Your system then receives updates on whether the order is filled, partially filled, or pending.
5. Feedback, Positions & Risk Control
Your program continuously receives order status updates via the API. Based on this:
- It updates positions
- Tracks profits and losses
- Manages risk (stop-losses, position limits, daily loss caps)
Good systems also handle errors like rejected orders or connection issues and can pause trading or alert you when needed.
6. Monitoring (Automation ≠ Blind Trading)
Even though execution is automated, human oversight is important. Most traders use:
- alerts (Telegram / email)
- logs
- simple dashboards
Automation handles execution, not responsibility.
Important India-Specific Note
Retail traders in India cannot connect directly to NSE/BSE/MCX/NCDEX. All automated trades must go through a broker’s API. Because of this, brokers enforce:
- rate limits
- risk controls
- order monitoring
Retail automation is best suited for low to medium-frequency strategies, not ultra-high-frequency trading.
In Short
Automated trading in India works like a fast, structured assembly line:
Your strategy decides → API communicates → Broker validates → Exchange executes → System reacts
Once you understand this flow, you understand how your code interacts with the real market.
Do you need coding to build a trading bot?
You don’t strictly need coding to build a basic trading bot, but having at least foundational programming knowledge is necessary for long-term success.
Step 1: Start with No-code AI/LLM driven approach: No-code, drag-and-drop platforms let beginners create simple strategies visually, much like assembling LEGO blocks, but they are often limited and can restrict creativity, flexibility, and adaptability. AI and LLMs now enable low-code approaches where strategies can be translated from plain English into code, lowering entry barriers.
Step 2: Move on to learning Python: You must understand core Python skills such as reading code, basic control flow (if–else, loops), functions, and how to debug errors to verify logic and prevent costly mistakes. Machines lack “common sense,” small logical errors can be costly. Relying fully on vendors to create bots risks IP exposure and slower deployment. For most traders, Python is sufficient, HFT-level languages aren’t necessary.
In 2026, we aren't just using "No-code"; we are using "AI Agents in Trading" that can optimize strategies.
Beginner Algo Trading Risk Checklist Before You Go Live
Note: This checklist is a practical sanity-check. Always verify broker requirements and applicable regulations.
Download the print ready checklist:
Final Thoughts: Is Automated Trading Worth It for Beginners?
Yes, but only if you drop the fantasy and respect the process. Automation works because it removes your biggest enemy: you. It makes trading boring, disciplined, and repeatable, and that’s exactly why it works. But it’s not an ATM machine you switch on and forget while you’re on a beach. You still need to monitor systems, adapt strategies as markets change, and understand what your code is doing. The good news? Barriers are lower than ever. You can start small, use visual tools, lean on AI for help, and avoid pointless battles like HFT. Treat algo trading like a business, not a lottery ticket and it can become one of the most powerful skills in your trading journey.
Treat algorithmic trading as a business.
Serious about learning?
EPAT is recommended for serious learners for those who are ready to commit to this field. A specialisation in algorithmic trading, it is often pursued by financial market participants who wish to embrace technology and AI in their work. It is a fully online course with 120+ hours of live lectures, a faculty pool of 20+ practitioners and experts from all over the world, with focus on Python and practical implementation. With dedicated mentorship, the programme enables participants of various backgrounds to join this exciting field.
Curriculum covered in EPAT is comprehensive and cutting edge, with lifetime access to improvements and additions to the curriculum.
How does QuantInsti help?
- Practical Innovation: The curriculum continuously evolves, integrating emerging financial technologies, machine learning, and crypto applications.
- Transparent & Credible Learning: A structured and practical approach that ensures real-world relevance and employer trust.
- Continuous Learning Mindset: A focus on upskilling and adaptability to stay ahead in dynamic financial markets.
- Career-Focused Approach: Every aspect of EPAT is built to enhance job readiness and professional growth.
Connect with an EPAT career counsellor to create a personalised quant career path for you
